What Are Cannabinoids?
Most weed lovers who enjoy smoking or vaping do not care to know what leads to the high feeling after a cloud of smoke or puff. Cannabis is made of small organic molecules, known as cannabinoids, responsible for what you feel.
It is quite understandable that this may not be a common term. However, you need to understand what your weed contains and why you are left feeling that way.
In this article, we will furnish you will all the information that you need to know regarding cannabinoids.
Table of Contents.
What are cannabinoids?
We first have to define what a cannabinoid is. Well, a cannabinoid is a member of the select group of chemicals named after the cannabis plant. What cannabinoids do to the body is to interact with specialised cells, generally known as cannabinoid receptors.
In case you are wondering what a cell receptor is, the simple answer is it is a specialised landing site found on the surfaces of the cell.
They are usually activated by chemical messengers released by the different systems of the body.
It wasn’t until 1964 that the structure of the first cannabinoid came into light. This was during joint research by Israeli doctors who were examining the cannabis plant.
Over the years, we have seen over 1113 similar structures all found in the mighty cannabis plant.
You should realise that this is one of the reasons why smoking or vaping marijuana causes a psychoactive effect. The discovery of this vital chemical paved the way for more research and examining the relationship between the two.
Your body has an endocrine system that is involved in the secretion and transportation of different hormones. While in the body, cannabinoids mimic the molecules that your body produces naturally, popularly referred to as the endocannabinoids.
In case you have been wondering where the psychoactive effect of weed stems from, here is a good start.
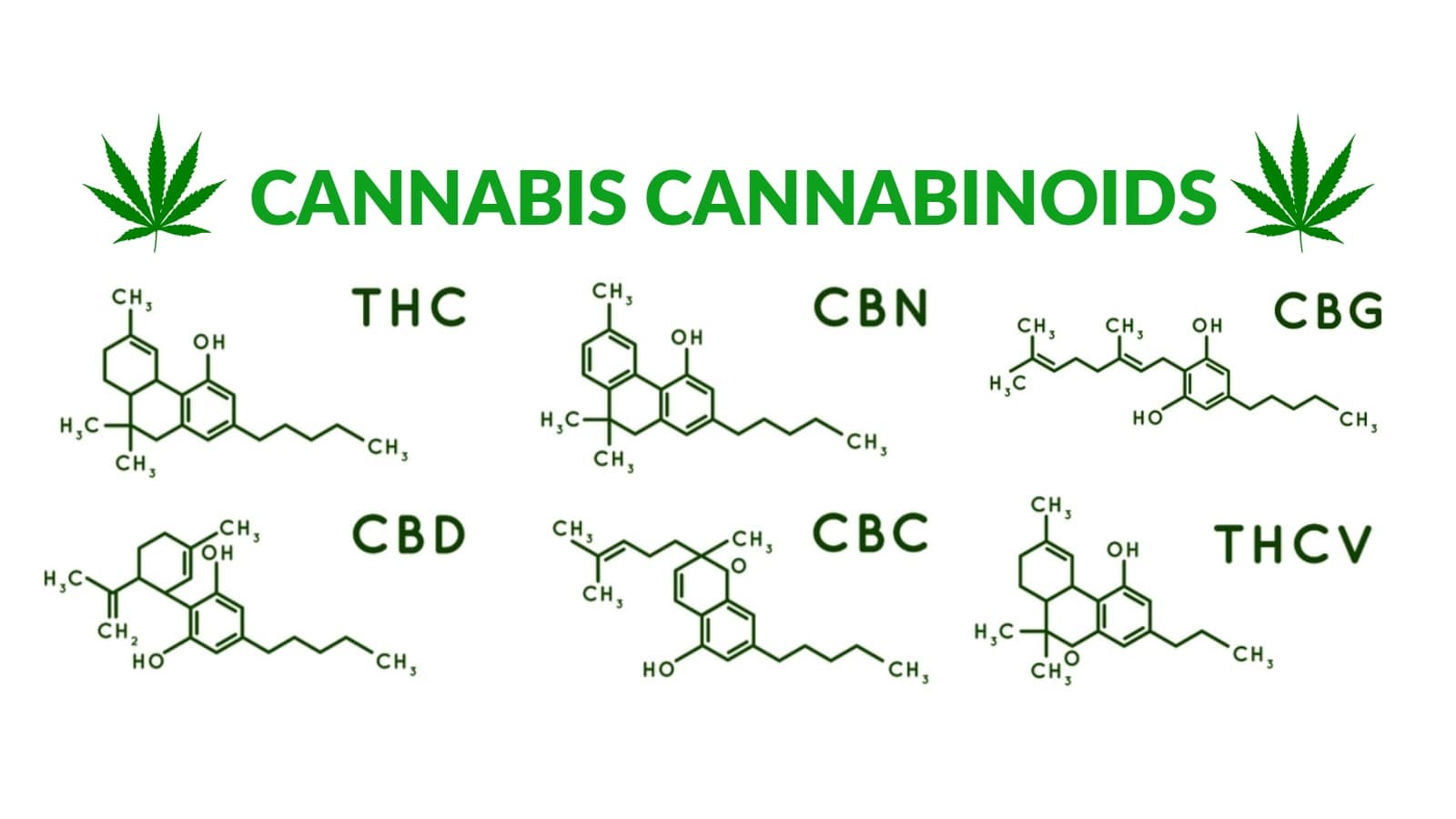
Types of cannabinoids
There are different types of cannabinoids. However, these are generally classified into three. It is quite easy to believe that these molecules are only produced by the cannabis plant, which is not true.
There are different sources of cannabinoids apart from cannabis. There are plant-based, animal-based, and human-made cannabinoids. To help you get a clear view of what we are talking about, let’s examine this further.
Phytocannabinoids
Just like the name suggests, phytocannabinoids compounds are found in plants. Out of all the plants in the universe, it is apparent that only cannabis is capable of producing cannabinoids and in large numbers.
There over one hundred cannabinoids in the cannabis plant. If you take marijuana, most of the cannabinoids present will engage either indirectly or directly with the cell receptors. The resultant effect is that the cells will undergo several chemical reactions, which is expected.
One of the most common effects of these reactions is intoxication. When you smoke weed, it releases different psychoactive effects through cell receptors known as cannabinoid receptors.
We will look at some of the compounds such as THC and how it makes you high.
Endocannabinoids
Endo means within. Therefore, endocannabinoids are naturally produced by the body. There are two types of main types; anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol.
Endocannabinoids, therefore, act as keys to the receptors. If you have heard of the endocannabinoid system, know that it is made up of endocannabinoids, cannabinoid receptors, and different specific enzyme proteins.
These molecules are usually charged with regulating different body activities, which should not come as a shocker since all vertebrates have an active endocannabinoid system.
Synthetic cannabinoids
Synethic cannabinoids are human-made molecules. Keep in mind that not all cannabinoids are produced naturally. Therefore, apart from the plant and animal-based, we have synthetic ones.
These cannabinoids are mostly used for scientific research and the manufacture of different medicines. One of the most famous synthetic cannabinoids is dronabinol, which is usually known as Marinol in the pharmaceutical market. Some of the uses of this compound include cancer management.
It mostly comes in handy in chemotherapy by relieving nausea and vomiting. It can also increase appetite in AIDS patients. Marinol is not the only synthetic cannabinoid.
Most of these compounds are used in the laboratory for research purposes, especially while studying the endocannabinoid system.
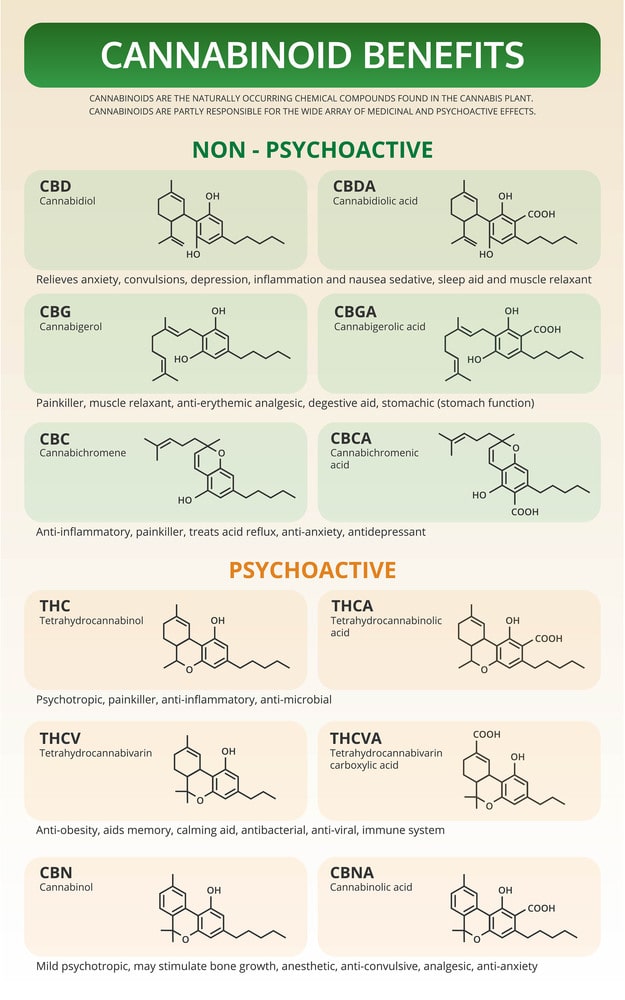
Cannabinoids found in cannabis
Cannabis contains several cannabinoids. Remember, it is one of the natural sources of cannabinoids alongside the human body. Despite having over one hundred different types of molecules, THC and CBD remain the most common cannabinoids in the cannabis plant.
Most cannabis oils and marijuana products have a high volume of either THC or CBD nor even both. Let’s explore these further:
1) THC
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the psychoactive agent in marijuana. It causes the ‘high’ effect that comes with marijuana intake.
This can either be the head high or the body high. For the body high, different parts of your body feel relaxed, and all you need is a rest. For the head high, your imaginations and senses are amplified.
There are speculations that this compound might be more helpful. Therefore, scientists are still exploring whether this compound can treat cancer, inflammation, nausea, pain, sleep, or spasticity.
If you are looking for a remedy, keep in mind that THC has not yet been approved for medicinal purposes.
2) CBD
Cannabidiol (CBD) is the acronym for cannabidiol. It comes second to THC in terms of quantity. There are several medical benefits that you can reap from this compound. Luckily, it is not intoxicating as the abundant counterpart.
There are different researches aimed at exploring whether the compound can remedy anxiety, pain, psychosis, inflation, pain, psychosis, seizure, among many other issues.
Several states have legalised this compound, and it is usually referred to as medical marijuana.
Even though these two compounds are the most abundant in the cannabis plant, they are not the only ones. There exist other cannabinoids in cannabis, mostly referred to as the secondary compounds since they can only be found in small concentrations.
These compounds are also believed to have little effects on the body but not as pronounced as THC or CBD. Little research has been conducted on these compounds due to their minimal impact on the body.
Most of the research conducted on these compounds are still in the early stages and are pre-conclusive.
Scientists do not also use humans when testing these compounds but instead rely on cell structures and animal specimen.
All in all, these compounds have several distinct properties that we should look at. Here are some of them:
3) CBC
CBC is known as Cannabichromene. It comes third in terms of quantity. However, in some instances, you may find that the level of CBC is higher than that of CBD.
Nevertheless, it remains a secondary or micro compound. Fortunately, it does not cause any type of intoxication. Research is undergoing to ascertain whether this compound can help fight cancer, inflammation, depression, and neuroprotection.
Since it is a minor compound, the research done is not as detailed as you would expect since most of these are done on animal specimens and not humans.
4) CBN
CBN is also referred to as Cannabinol. It comes from THC, which generally converts to this compound as the cannabis flower ages and dries up. The level of CBN in these flowers increases depending on the duration of drying and curing.
Just like all the other compounds, scientists are still trying to prove whether CBN can effectively help in appetite stimulation, inflammation, pain relief, neuroprotection, and whether it has antibiotic effects.
Most people believe that this compound has sedative effects, which we cannot overrule. However, this is mostly seen when it is combined with THC.
CBG This compound is mostly seen when the cannabis plant is in the early stages of development. It cannot, therefore, be found in large quantities.
It does not have a psychoactive effect, as seen in THC. Scientists are still examining whether this compound can help relieve pain, inflammation and whether it has antibiotic properties.
5) TGCv
This compound is closely related to THC. However, research has proven that it counters the impacts of THC. It is being examined whether it can treat seizures, diabetes, and offer neuroprotection.
6) CBDv
The CBDv compound is similar to CBD only that it has a different structure. Scientists are conducting tests to determine whether it can treat nausea and seizure.
7) Delta 8-THC
The delta 8-tetrahydrocannabinol molecule differs slightly from THC because of a lower ‘high effect’. It is not as common and comes in small concentrations.
Scientists are still trying to determine whether it can help fix appetite, nausea, and contribute to neuroprotection.
Raw cannabinoids
There are two raw cannabinoids that we need to talk about. These are mostly used as dietary cannabinoids and can be found in smoothies, raw cannabis tinctures, and juices.
1) THC-acid
Unlike THC, THC-acid is non-intoxicating. It is mostly found in raw and unheated cannabis plants and acts as a precursor to THC.
At the moment, scientists are still trying to determine whether this compound can help deal with cancer, inflammation, nausea, and seizure.
2) CBD-acid
Just like THC-acid, this is a precursor to CBD. CBD-acid is only found in unheated cannabis. At the moment, this compound is being examined for cancer and nausea prevention and treat.

James King
James is an experienced writer and legal cannabis advocate in Australia. He answers all the questions about business, legalisation and medicinal cannabis.
Disclaimer: Cannabis Place are not doctors and we recommend consulting health professionals for accurate information. This site may contain information regarding drugs. This medicinal cannabis content is designed for an 18+ audience. Click here for our full disclaimer




